What Industries Commonly Use Electromagnetic Lifters? High-Efficiency Handling for Heavy Steel Movements
In metal machining and recycling, secure workholding directly impacts precision, productivity, and safety. The electromagnetic chuck is a compact yet highly effective solution — delivering strong magnetic grip and fast release for steel and iron workpieces, helping operations run smoother and more efficiently.

Industries That Commonly Use Electromagnetic Lifters
1. Scrap Metal Recycling & Processing Facilities
Electromagnetic Lifters are widely used for high-volume scrap handling.
Typical activities include:
-
Bulk scrap loading
-
Furnace charge preparation
-
Feeding shredders, shears, and balers
-
Sorting and transferring mixed scrap
Companies can reduce yard handling time by 50% or more.
2. Steel Mills & Foundries
Industries with continuous steel flow rely heavily on magnetic handling systems.
Applications include:
-
Slab and billet movement
-
Coil and sheet transfer
-
Rolling mill feed operations
-
Casting line handling
Heavy-duty models are often specified between 10 to 32 tons.
3. Ports, Warehouses & Logistics Terminals
Facilities moving steel at scale benefit from:
-
Faster loading
-
Safer material transfer
-
Reduced forklift reliance
Electromagnetic Lifting enables higher throughput and lower accident rates.
4. Auto Dismantling & ELV Centers
Electromagnetic lifters are used for:
-
Vehicle body handling
-
Engine block removal
-
Scrap sorting
Cycle efficiency improves significantly due to fast release.
5. Shipyards & Marine Engineering
These facilities frequently lift:
-
Hull plates
-
Framing structures
-
Large fabricated parts
Often integrated with gantry cranes and overhead cranes.
6. Metal Fabrication & Heavy Processing Plants
Especially valuable for:
-
Cutting tables
-
CNC plate processing
-
Material repositioning
They reduce manual handling and improve machining workflow.
Key Advantages of Electromagnetic Lifters
Operational Benefits
-
Increased handling speed
-
Minimal surface damage
-
Reduced labor dependency
-
Higher material throughput
Safety Advantages
-
No manual hooks or chains needed
-
Lower handling risks
-
Controlled magnetic force
Financial Benefits
-
Reduced operational downtime
-
Lower logistics costs
-
Increased equipment utilization
How to Choose the Right Electromagnetic Lifter
Key criteria include:
-
Material type and geometry
-
Weight and lifting height
-
Duty cycle requirements
-
Environmental climate (heat, humidity, dust)
-
Power supply compatibility
-
Integration method (crane, gantry, beam system)
Correct sizing ensures longer service life and stable performance.
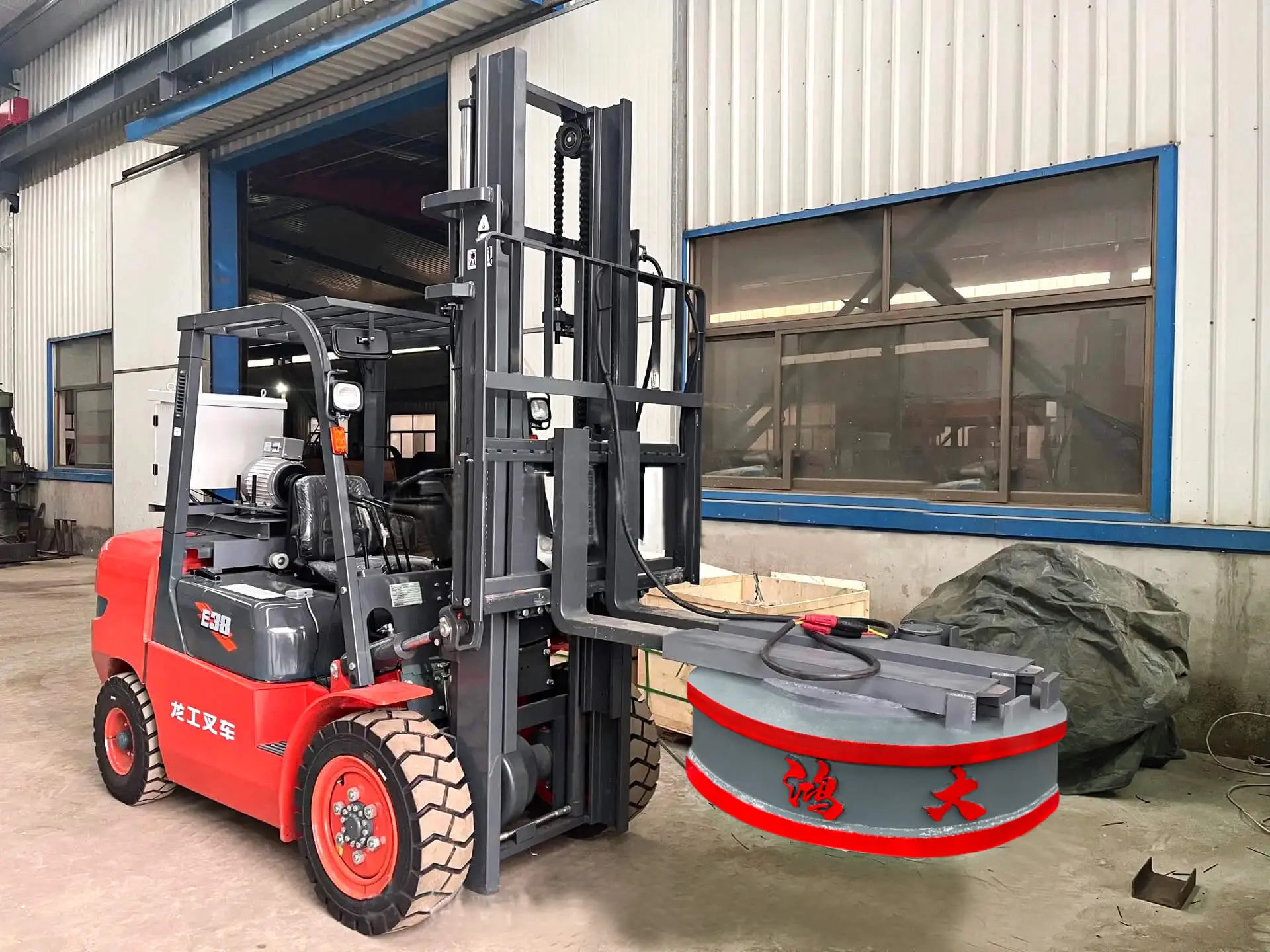

Electromagnetic lifters are essential in industries where steel movement and heavy material handling occur daily. From recycling plants to ports, steel mills, and fabrication shops, these systems significantly enhance handling efficiency, safety, and operational continuity. With the right specification and setup, companies can reduce labor intensity, increase throughput, and achieve consistent handling performance.
FAQs
Q1: What industries commonly use electromagnetic lifters?
Recycling companies, steel mills, shipyards, auto dismantling yards, ports, and metal fabrication plants regularly use electromagnetic lifting systems.
Q2: What materials can electromagnetic lifters lift?
Carbon steel, alloy steel, cast iron, steel plates, billets, pipes, and mixed scrap metal.
Q3: Are electromagnetic lifters safe for continuous operation?
Yes, industrial-grade units are designed for 24-hour duty cycles with appropriate cooling systems.
Q4: How long does an electromagnetic lifter last?
Typically 8 to 12 years, depending on usage intensity and maintenance discipline.