Electromagnetic Chuck: Efficient Workholding for Metal Processing
In metal machining and recycling, secure workholding directly impacts precision, productivity, and safety. The electromagnetic chuck is a compact yet highly effective solution — delivering strong magnetic grip and fast release for steel and iron workpieces, helping operations run smoother and more efficiently.
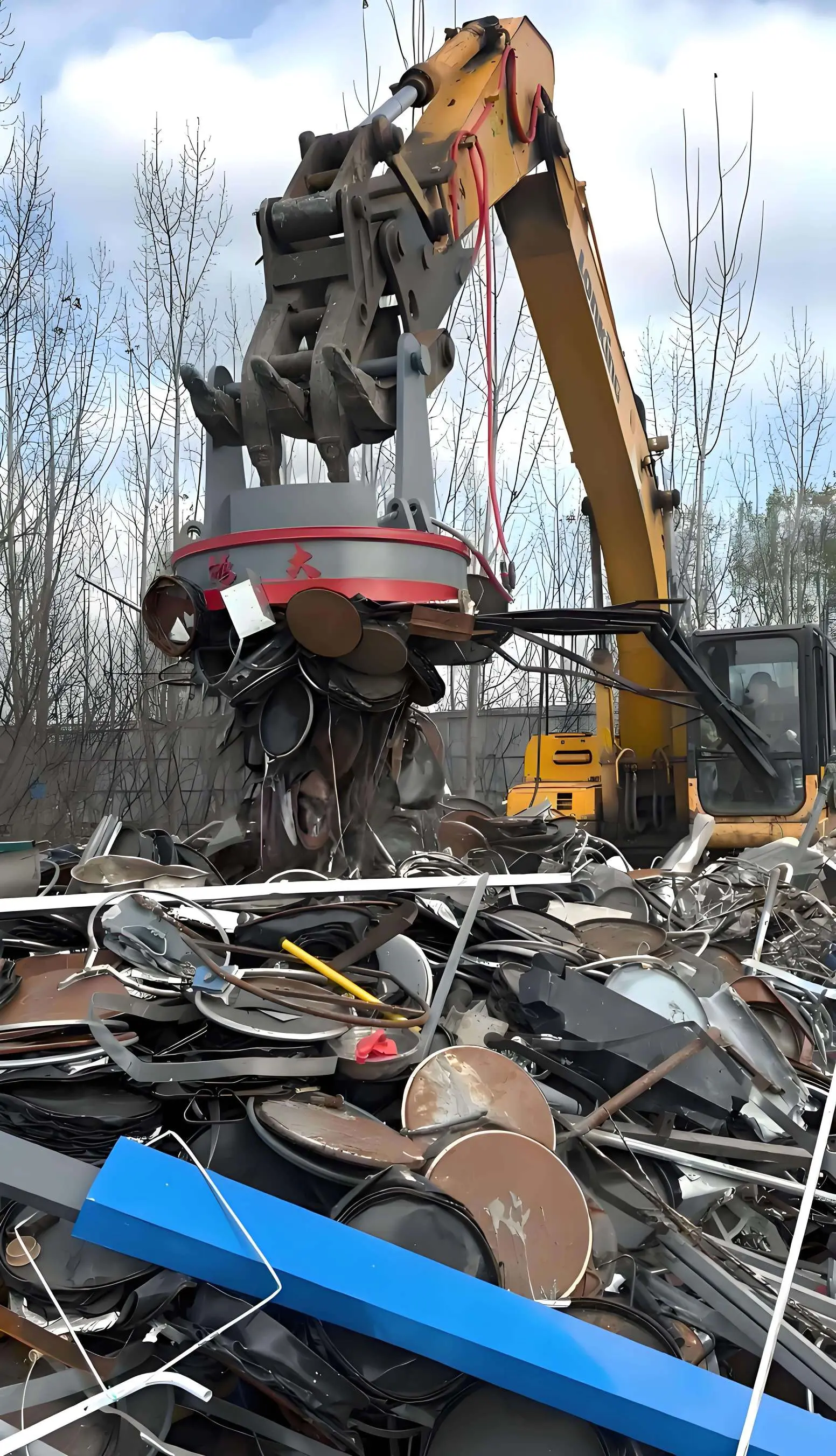

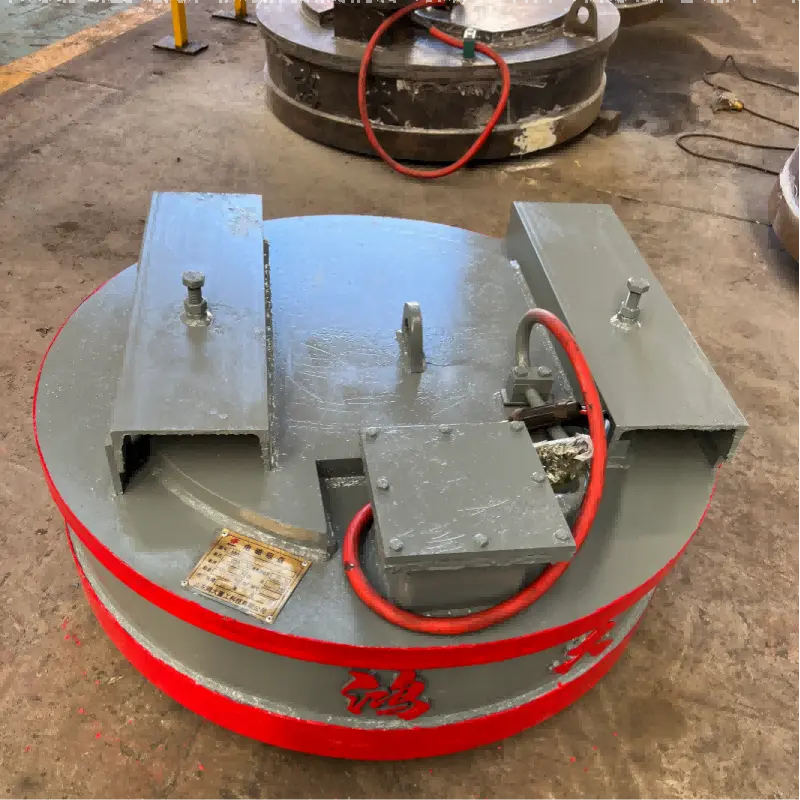
What Is an Electromagnetic Chuck?
An electromagnetic chuck uses electrically generated magnetic force to hold ferrous materials firmly during cutting, grinding, or lifting.
When powered on, it grabs; when the power stops, materials are instantly released.
Core Components
-
Magnetic Coil — Creates the magnetic field.
-
Steel Pole Plate — Transfers magnetic force to the workpiece.
-
Control Unit — Adjusts power and holding strength.
How It Works (Simple Principle)
1️⃣ Current flows through the copper coil.
2️⃣ A magnetic field forms and magnetizes the steel poles.
3️⃣ The workpiece locks securely in place.
4️⃣ Power off → magnetic force disappears → quick release.
This process eliminates clamp marks and reduces setup time by 20–40%, enabling higher cutting speed and improved surface finish.
Key Specifications (Typical Ranges)
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Magnetic Force | 100–160 N/cm² |
| Voltage | 110V / 220V DC |
| Pole Pitch | 1.5–8 mm (optional) |
| Cooling Method | Air- or oil-cooled |
| Residual Magnetism | ≤2% after release |
| Sizes | 200×400 mm up to 1500×3000 mm |
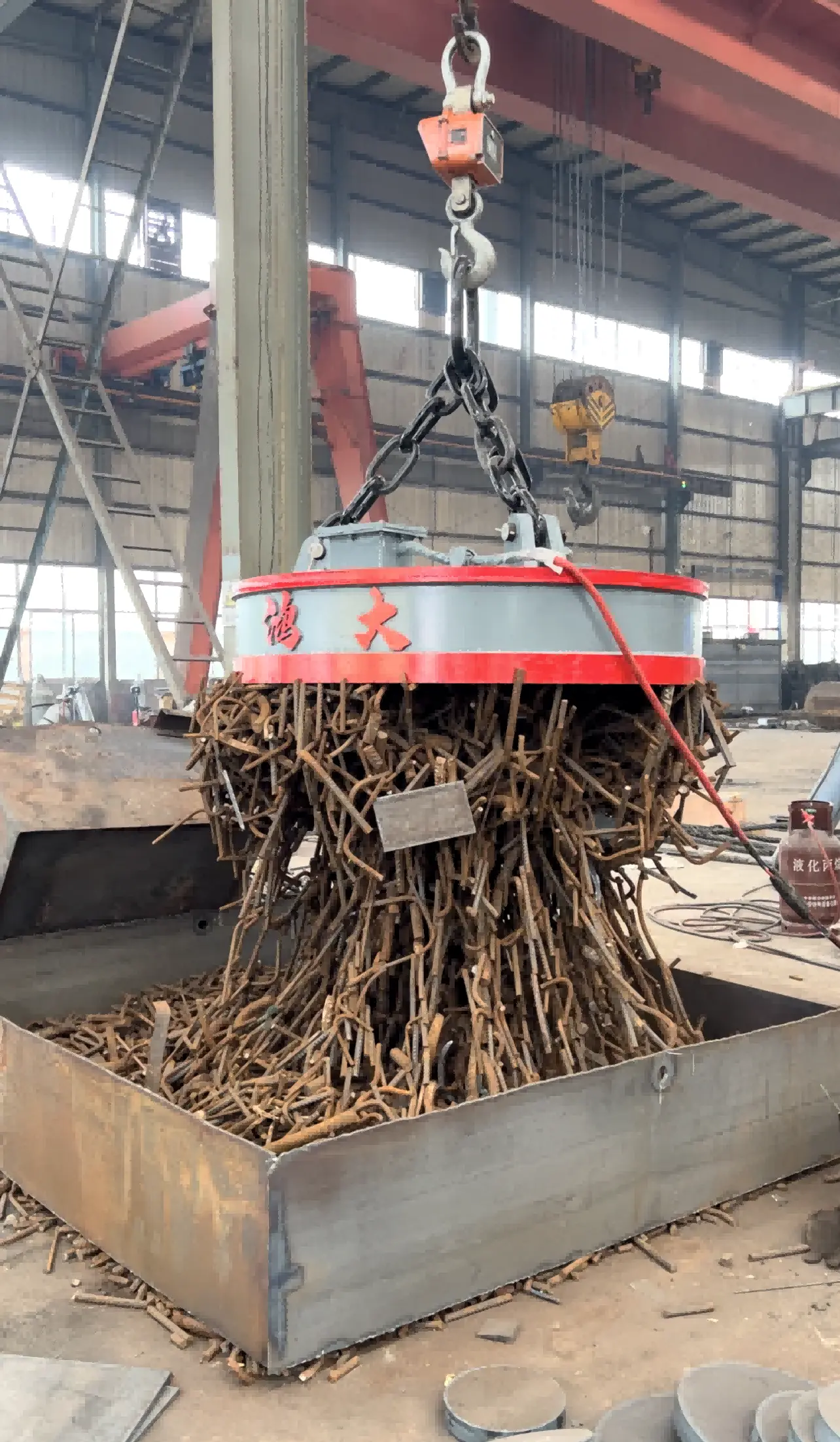

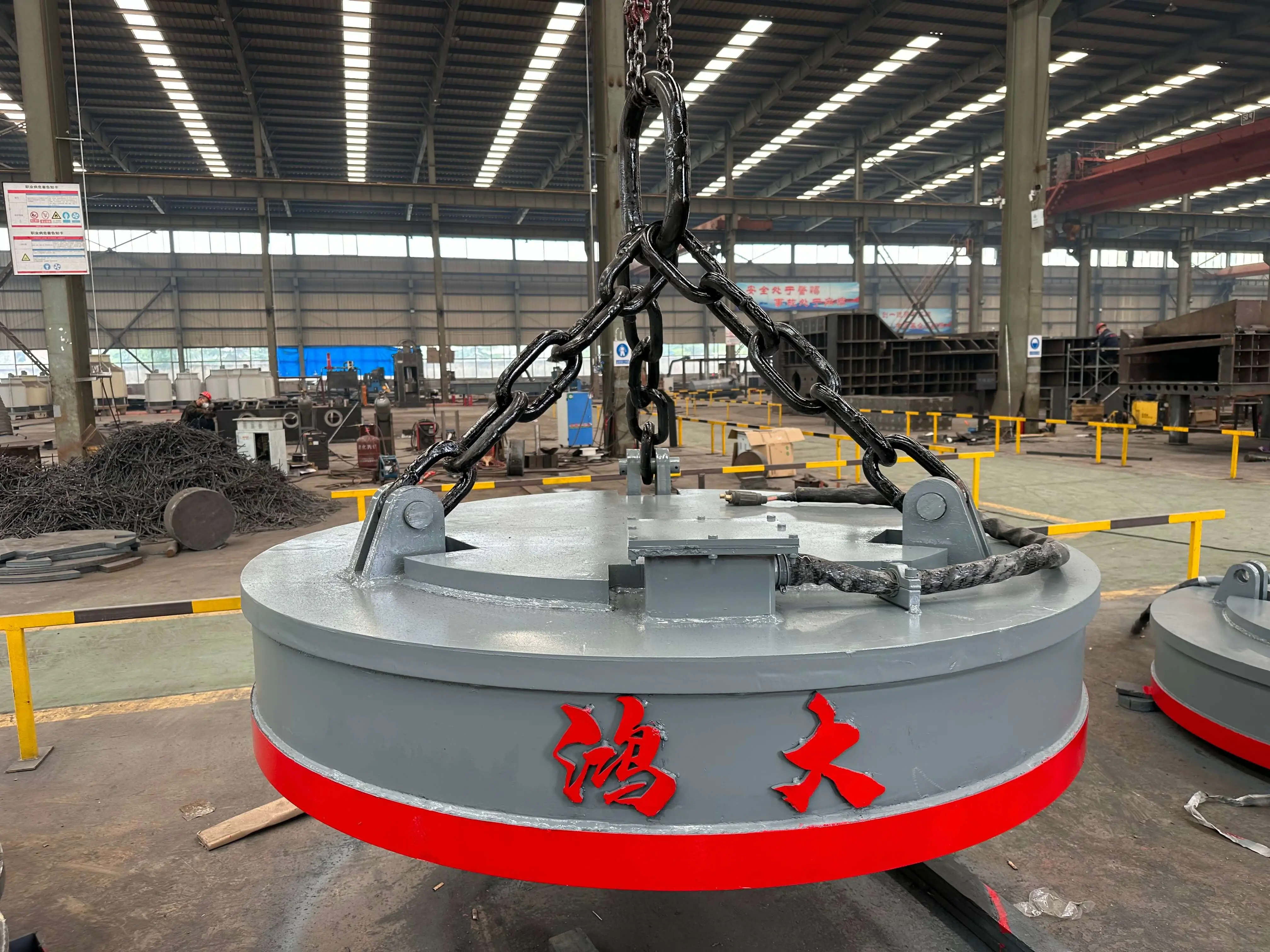
Where It’s Used
Electromagnetic chucks are widely applied in:
-
Surface grinding & CNC machining
-
Billet and steel plate cutting
-
Scrap Lifting in recycling operations
-
Vehicle dismantling & heavy logistics handling
For mixed-metal operations, it can be combined with clamps or lifting attachments for extra flexibility.
Why Choose Electromagnetic Chucks?
Higher Accuracy — No mechanical deformation.
Faster Workflow — Reduced changing and fixturing time.
Energy-Efficient — Low-voltage control systems.
Safer Operation — Automatic demagnetization after power-off.
Custom Designs — Round, rectangular, and lifting types available.
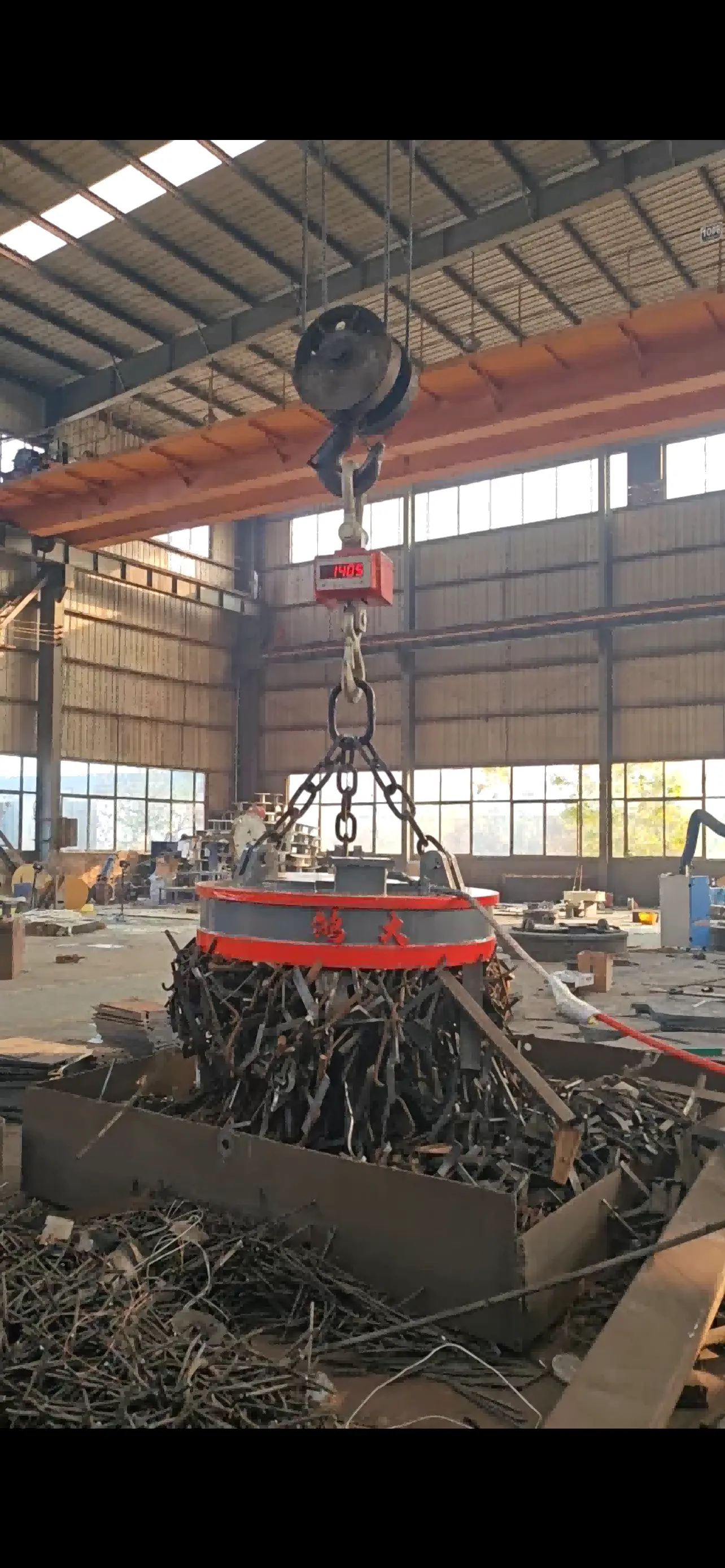

How to Select the Right Model
Consider the following factors when choosing an electromagnetic chuck:
✔ Workpiece Size, Thickness, and Weight
✔ Processing Type — Grinding uses fine poles; lifting uses heavy coils.
✔ Operating Environment — Heat, dust, outdoor, or moisture exposure.
✔ Duty Cycle — Continuous or intermittent operation.
✔ Control System Compatibility — Ensure safety and voltage match.
The electromagnetic chuck enhances machining precision, reduces downtime, and improves safety in modern metalworking and recycling operations.
By selecting the right model, manufacturers can achieve long-lasting performance and a clear boost in operational efficiency.
FAQs
Q1: What materials are supported?
Ferromagnetic metals such as steel and iron. Other materials require alternative clamping systems.
Q2: What’s the difference between electromagnetic and permanent magnetic chucks?
Electromagnetic models require power to magnetize and release, offering better control and flexibility for variable workloads.
Q3: How long is the service life?
Approximately 8–12 years with proper use and regular maintenance.
Q4: Can it operate continuously?
Yes — industrial-grade chucks can run 24/7 with stable power and cooling systems.